Chronological Evolution of Computerized Decision Support to Business Intelligence, Analytics, Data Science
Introduction
From the earliest know examples from human history of the barter system that eventually evolved to modern-day corporations, businesses have always looked for a way to manage, improve and mitigate risk in their trade and operations. This requirement warranted a system for the business that would help achieve maintenance and growth. This started off an evolutionary path from the early Computerized Decision Support systems to modern-day Business Intelligence, Analytics, and Data Science.
It wasn't until the 1960s that the journey began with building model-driven DSS, then theory developments in the 1970s, and implementation of financial planning systems, spreadsheet-based DSS, and Group DSS in the early and mid-1980s (Power, D.J., 2007, p.1).
A Longitudinal View of Analytics:
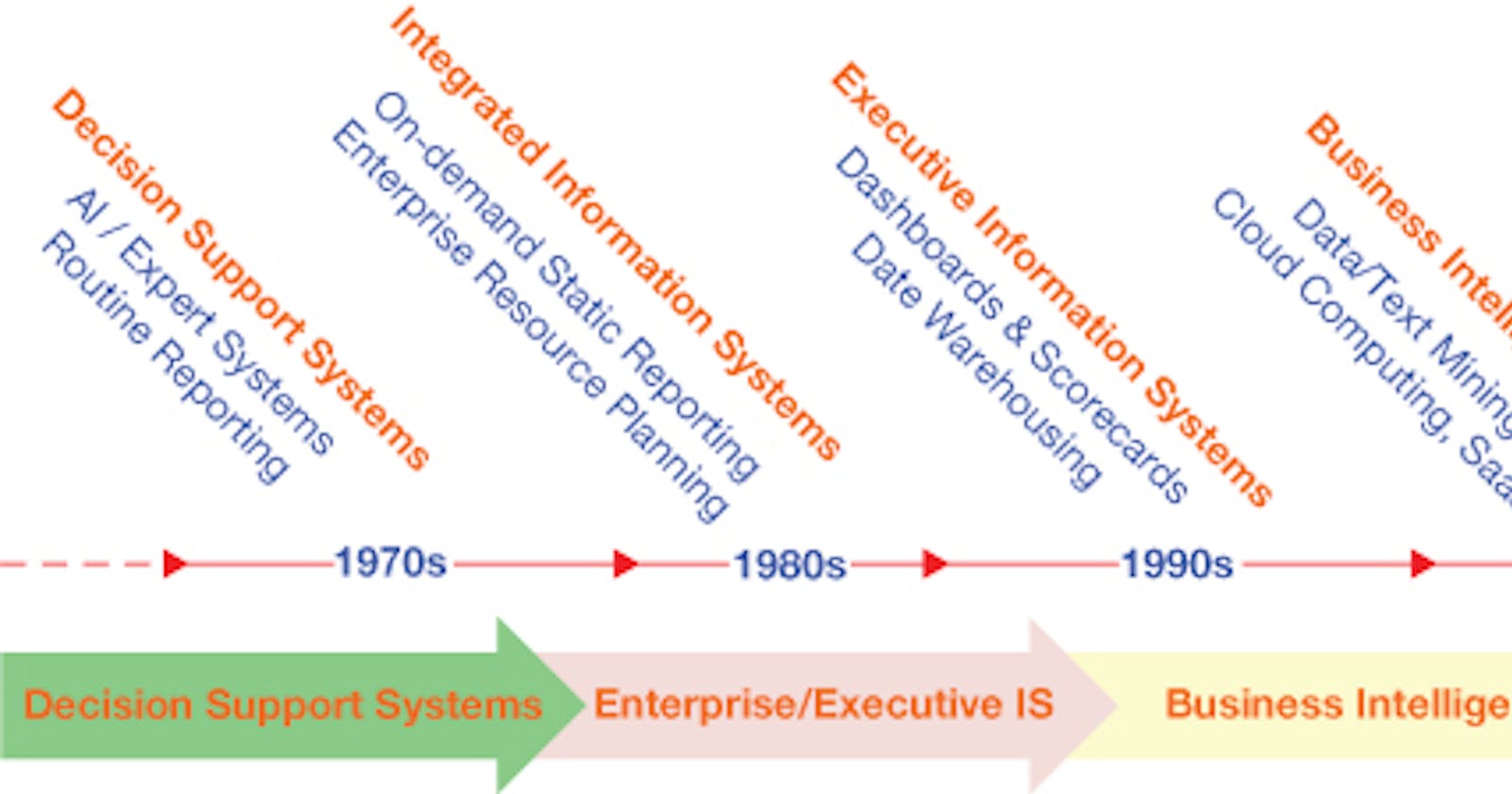
Chronologically the evolution can be categorized roughly as under:
- The 1970s Decision Support System, AI/Expert Systems, and Routine Reporting During the 1970s, the information system focused mainly on providing structured, periodic reports used for decision-making. These were mostly historical records that were used for the analysis of past performance. During the early days of analytics, data was often obtained from domain experts using manual processes. This expert knowledge was captured in a machine-processable form to identify the structured problem and prescribe the most probable solution.
- The 1980s Integrated Information System: On-demand static reporting, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) A significant change was seen as data captured in isolated Business Units (BU) like accounting, marketing, sales, finance, manufacturing, etc were now aggregated for an enterprise-level IS now commonly known as an ERP system. The old nonstandardized data representation schema was now replaced by a relational database management system (RDBMS)
- The 1990s Executive Information System: Dashboards & Scorecards and data warehousing.
- The 2000s Business Intelligence: Data/Text Mining, cloud computing, and SaaS (software as a service)
- The 2010s Business Analytics and Big Data Analytics: Social Network/Media Analytics
- The 2020s Automated Analytics: Robotics, Smart Robo-assistants, AI, Deep Learning, Sensors.
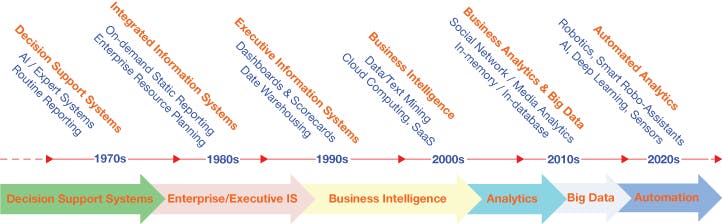
FIGURE: A longitudinal view of the evolution of analytics (Delen. D, 2019, p.4-9).
Conclusion
Coming to the modern day, analytic systems are evolving at a much faster rate than the managers in the loop might even struggle to cope with the fast pace of adoption. Hence a system called CHROMA model had to be developed to evaluate whether the management of organizations is making decisions using the available data correctly and optimizing their information systems" (Xileidys Parra1, Xavier Tort‑Martorell1, Fernando Alvarez-Gomez, Carmen Ruiz-Viñals, 2022, p.1).
References:
Delen, D. (2019). Prescriptive Analytics: The Final Frontier for Evidence-Based Management and Optimal Decision Making (1st ed.). Pearson FT Press.
Dursun Delen, Prescriptive Analytics: The Final Frontier for Evidence-Based Management and Optimal Decision Making 1st Edition (2019) informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=299260..
Power, D.J. A Brief History of Decision Support Systems. DSSResources.COM, World Wide Web, DSSResources.COM/history/dsshistory.html, version 4.0, March 10, 2007.
Xileidys Parra1, Xavier Tort‑Martorell1, Fernando Alvarez-Gomez, Carmen Ruiz-Viñals. (2022). Chronological Evolution of the Information‑Driven Decision‑Making Process (1950–2020). link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s1313.. (pdf)